Updated December 2025
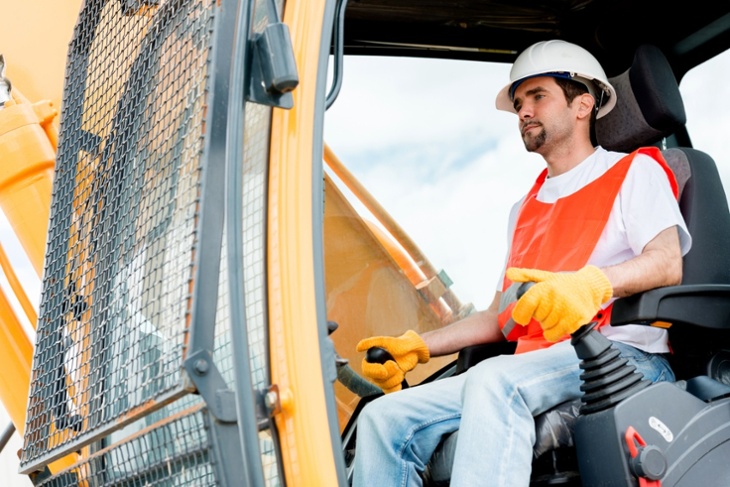
Students enrolling in pre-apprenticeship training should expect site safety to be a major feature of both theory and hands-on coursework.
Construction professionals in Ontario are compelled to meet specific safety training and certification requirements. Quality trades colleges introduce and reinforce those standards from day one of training, ensuring pre-apprentices are equipped with the fundamentals employers look for—the safety knowledge needed to protect themselves, colleagues, and the public while working.
Wondering what kinds of safety practices you will learn in pre-apprenticeship training?
Start by understanding some of the most common job site injuries, and why safety education is key for preventing accidents.
1. Falling from Heights
In Canada, more than 40,000 construction workers get hurt every year due to fall accidents. Injuries from falls account for a large number of worker compensation claims, and in the most serious cases, result in significant back and spinal cord problems, paralysis, and even death.
What are the most common causes of falls on construction sites? Contributing factors include:
- Missing guardrails
- Missing fall-protection equipment, or lack of education on how to use the equipment
- Ladders and scaffolds that are in poor condition, or not used correctly
- Lack of worker safety training
Taking (or considering taking) a pre-apprenticeship program for construction and maintenance electrician, carpentry, HVAC, or plumbing? Your courses should include safety training for working with scaffolds and at heights.
Typical topics in these areas of construction safety include:
- How to safely erect, use, modify, and dismantle scaffolds
- Scaffold safety guards, platforms, and access
- How to identify, eliminate, or control the hazards of working at heights
- Personal fall protection systems and rescue planning
2. Burns
Burns are another common site injury that can often be prevented with the right safety measures. Typical causes of burns include bad wiring, corrosive chemicals that aren't handled correctly, and undiagnosed gas leaks.
Other common fire and explosive hazards on construction sites include:
- Mishandling of flammable and combustible liquids
- Inappropriate use of temporary heating devices
- Accidents with explosives and blasting agents
- Arc flashes and blasts
- Pressurized container explosions
Anyone following pre-apprenticeship programs for gas technician training, plumbing, and HVAC should learn how to safely handle propane and natural gas—and refrigerants (where applicable), which can be toxic and flammable.
3. Electric Shock & Electrocution
Lack of awareness is a major contributor to electrical-related construction injuries. Too many workers simply don't recognize the electrical hazards present on the job site and do not apply the correct steps to control or eliminate these dangers.
The most common causes of electric shock and electrocution for construction workers include:
- Working near live wires
- Failing to de-energize power sources using lockout/tagout procedures
- Lack of basic electrical safety knowledge (such as lockout/tagout)
- Failing to avoid live overhead power lines
- Continuing to work with worn, frayed, torn, or otherwise damaged electrical cords, cables, outlets, etc.
Almost all of today's pre-apprenticeship training programs include at least basic electrical training and ensure students understand the electrical safety requirements of the Occupational Health and Safety Act.
4. Cuts, Broken Bones & Head Injuries
This broad category of worksite injuries may include anything from non-threatening wounds to life-altering and potentially fatal accidents. Cuts, lacerations, broken bones, and head injuries may be caused by a number of poor site safety practices, including:
- Poorly maintained tools
- Exposed nails
- Machines that have not been correctly secured/de-energized
- Falling objects
- A cluttered workspace where tools and debris become tripping/falling hazards
One of the biggest issues is failure to wear proper protective gear that can help safeguard workers from accidents. Gear varies depending on the job at hand, but a typical kit usually includes:
- Hard hats
- Gloves
- Safety boots
- Safety glasses
- Safety harnesses
- Non-skid footwear (for wet or slippery surfaces)
Pre-apprenticeship training introduces students to the use and critical importance of safety gear. Protective items are always worn during hands-on training, setting in motion what should become a lifelong habit and baseline safety standard for all construction professionals.
Interested in learning more about cutting-edge pre-apprenticeship training programs?
Your next step is to speak with Herzing College admissions. An advisor will guide you through our available skilled trades programs and answer all your questions about costs, financial aid, and what to do next.
Chat live with an advisor right now. Or request program information by email. We're here to help!